Treatment of Advances received under GST
Under GST laws, the concept ‘Time of Supply’ has been introduced for deciding the point of taxation in respect of supply of goods & services. Section-12(2) of CGST Act states the rules for ‘Time of Supply’ for supply of goods whereas Section 13(2) of the Act gives rules for ‘Time of Supply’ for supply of services. Thus, the rules for ‘Time of Supply’ of goods and of services are different. In general, ‘Time of Supply’ is linked with date of issue of invoice or date of receipt of payment.
In simple terms, in case of supply of goods or services, the ‘Time of Supply’ shall be the earlier of date of invoice or date of receipt of payment by the supplier. However, in case of supply of services, if the invoice is not issued within the prescribed time limit of 30 days, the ‘Time of Supply’ shall be the earlier of the date of provision of service or date of receipt of payment by the supplier.
To summarize, if the supplier is receiving any payment in advance for supply of goods or services before raising the invoice or before provision of service, he is required to discharge tax liability on such advance as well even if no actual sale has been made as yet. Even if a part advance is received, then the ‘Time of Supply’ for such advance is at the time of receipt of advance and for the balance amount, the time of supply will depend on the date of issue of invoice. If transaction is cancelled after receipt of advance, then the advance so received needs to be refunded or adjusted or forfeited for later supplies.
No GST on advances against supply of Goods
(a) CBIC issued a Notification No. 66/2017 dated 15-11-2017 which exempts the suppliers of goods (other than composition dealers) from levy of GST on advance receipts.
(b) This exemption was allowed recognizing the difficulties faced by the small businessmen with compliance burden involved due to GST on advances.
(c) Thus, any supplier of goods (other than composition dealer) need not pay any GST on advances. Thus, ‘Time of Supply’ for supply of goods shall be the date of issue of invoice.
(d) But it should be kept in mind that this relaxation is not available for service providers. They shall continue to pay GST on advance receipts.
(e) Further, the above notification is not applicable on registered dealers under composition levy.
Treatment of Advance receipts by supplier of services in his books
(a) According to Section 31(3) of CGST Act, 2017, a registered person shall, on receipt of advance payment issue a receipt voucher or any other document which contains details as prescribed in Rule 50 of CGST Rules. Such details are amount of advance, tax rate as applicable, description of goods or services etc.
(b) If supply is not made subsequent to receipt of advance, then the advance may be refunded back and refund voucher shall be issued.
How to calculate GST payable on advances received
(a) The advances received by the supplier shall be considered as inclusive of GST.
(b) Rule- 50 of CGST Rules states that when the tax rate is not determinable, GST on advances shall be charged @ 18%.
(c) Also, if the nature of supply is not determinable in case of advances, it shall be treated as an inter-state supply.
We will take an example to understand calculation mechanism of GST on advances:
Mr. Ramesh entered into a contract to provide service to Mr. Suresh. Contract value is Rs. 50,000 and GST rate is 18% (Total Rs. 59,000 including GST). He receives an advance of Rs. 10,000 on 15-01-2021 and balance consideration of Rs. 49,000 on 27-02-2021. Date of issuing invoice is 24-02-2021.
Calculation of GST: -
|
Relevant Date |
Total Consideration |
GST Element |
Basic Invoice Value |
Time of Supply |
|
15-01-2021 |
10,000 |
1525 (10,000 * 18/118) |
8475 (10,000- 1525) |
15th January (Time of Supply is date of advance received) |
|
24-02-2021 |
49,000 |
7475 (49000* 18/118) |
41,525 (49,000- 7475) |
24th February (Time of Supply is date of invoice or date of receipt whichever is earlier) |
|
Total |
59,000 |
9,000 |
50,000 |
|
Therefore, Mr. Ramesh will pay GST Rs. 1525 in respect of January 2021 and GST Rs. 7475 in respect of February, 2021. It is also important to note that Mr. Suresh cannot claim ITC of GST on advances paid. He shall be eligible to claim ITC Rs. 9,000 only in the month of February, 2021.
How to show GST on advances in GSTR-1
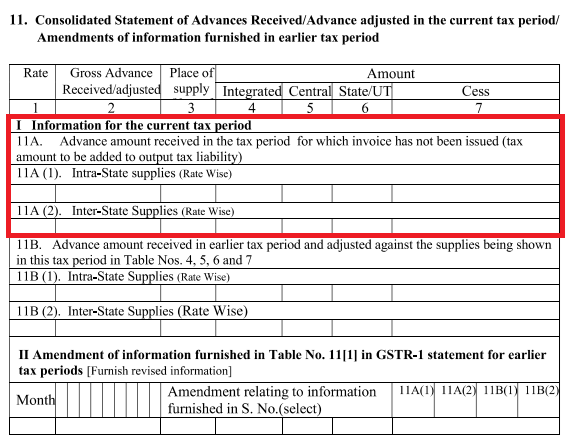
(a) Table-11 of GSTR-1 requires the disclosure of the details of advances received/ adjusted.
(b) Any advances received for which invoice has not been issued needs to be shown in Part- 11A of GSTR-1. Details of advance is not given party-wise but aggregate amount of advances received has to be given. Further, the aggregate amount of advances is to be segregated into intra-state and inter-state.
(c) In Part-11B of GSTR-1, the details of advance amount received in earlier tax period and adjusted against the supplies in the current tax period is to be given.
Other important points:
GST rates on various goods and services have changed since introduction of GST. Some items which were earlier in 28% bracket have been brought now in 5% 0r 12% or 18% bracket. To handle such situation in respect of advances, Notification No. 41/2017 dated 14-11-2017 provides that if the GST rate at the time of advance receipts is higher (say 28%) and later it is reduced at the time of issue of invoice (say 18%), such excess GST paid on advances may be adjusted at the time of raising invoice against that supply or may be claimed as refund.
Related Posts:
Time of supply under GST for supply of services
How to issue tax invoices for services under GST



