Income Tax Provisions for Doctors
Introduction:
It is commonly seen that medical practitioners are so busy in their professional commitments that they often neglect their tax planning and compliances. This leads to unnecessary financial burden and litigations in future in form of income tax notices & demands. Looking into the problems faced by the medical practitioners, we have compiled all the requirements of the Income Tax Act, 1961 from the point of view of doctors in this article so that they could make timely compliances of the Income tax law in India.
What are the prescribed Books of Accounts to be maintained by doctors
Section 44AA of the Income Tax Act prescribes that the medical professionals shall maintain the books of accounts so that their total income could be computed by the Income Tax Officer.
Following books of accounts have been prescribed by Rule 6F in respect of medical practitioners:
- Cash Book
- Journal (if mercantile system of accounting)
- Ledger
- Carbon copies of bills (in excess of Rs. 25), whether machine numbered or serially numbered
- Original Bills wherever issued to the person and receipts in respect of expenditure incurred or, where such bills and receipts are not issued and the expenditure incurred does not exceed Rs. 50, payment vouchers prepared and duly signed.
In addition to above, the medical practitioners shall also keep and maintain the following namely:
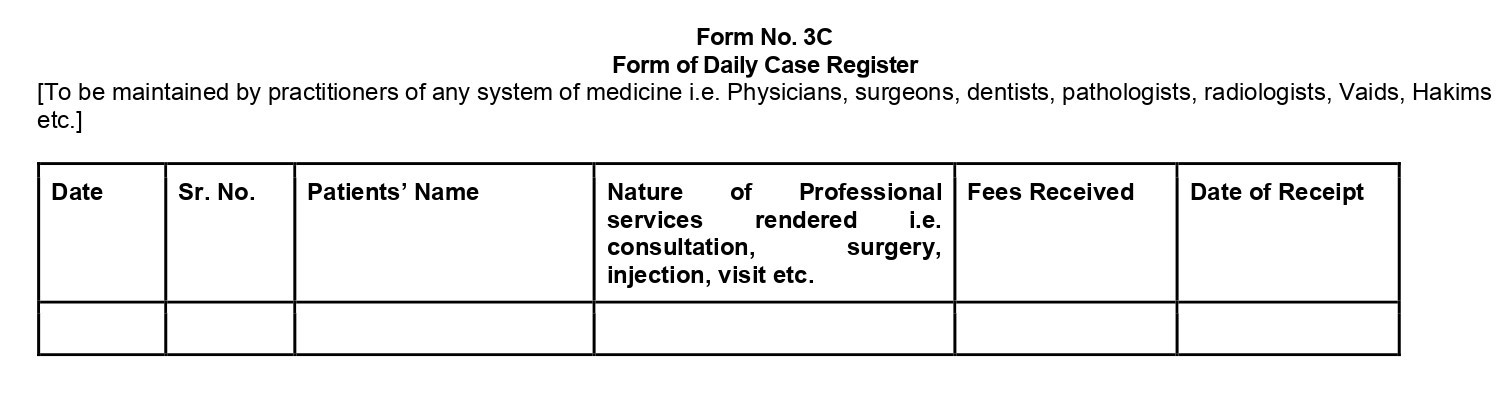
- A Daily Case Register in Form No. 3C
- Inventory Register showing stock (as on first day and last day of the year) of drugs, medicines and other consumables used for the purpose of his profession.
When are doctors not required to maintain prescribed books of accounts under Rule 6F
The medical practitioners are not required to keep and maintain the prescribed books of accounts in the following cases:
- In case of newly set up profession: If the profession has been newly set up in the financial year and gross receipts for that year are not likely to exceed Rs. 1,50,000
- In case of existing profession: If gross receipts from medical profession does not exceed Rs. 1,50,000 in any of the last 3 financial years immediately preceding the relevant financial year.
Where shall books of accounts be kept and maintained by the doctors
- The medical practitioners shall keep separate books of accounts in respect of each place where he carries on his profession.
- Such books of accounts and other documents may be kept and maintained at the respective places at which the profession is carried on (like clinic).
What is the time limit for keeping the books of accounts and other records for a particular year
The books of accounts and other prescribed documents shall be kept and maintained for a period of 6 years from the end of the relevant assessment year. For example: In respect of F.Y. 2021-22, the relevant assessment year is 2022-23. So, the books of accounts & other records relating to F.Y. 2021-22 shall be kept till 31-03-29.
What is the due date of filing income tax return for the medical practitioners
- Due date of filing Income Tax Return:
(a) Non-Audit Cases: 31st July after the end of the relevant financial year.
(b) Audit Cases: - 31st October after the end of the relevant financial year - However, For F.Y. 2020-21, the due date of filing ITR has been extended to 30th September, 2021 (non-audit cases) & 30th November, 2021 (audit cases) due to Covid-19 pandemic. [updated till the date of publishing this blog]
Is audit compulsory in case of doctors under Income Tax Act
There are two situations in which the audit is required in case of medical practitioners:
- Case -1: The medical practitioners are required to get their accounts audited by a practising Chartered Accountant if their gross receipts during the financial year exceeds Rs. 50 Lakhs OR
- Case-2: If the gross receipts does not exceed Rs. 50 Lakhs but you claim a profit lower than 50% of gross receipts and total income exceeds maximum amount which is not chargeable to income tax i.e. Rs. 2.50 Lakhs (in case of individual).
Due date of audit under Income Tax Act is 30th September after the end of the relevant financial year. However, due to Covid-19 pandemic, due date of audit has been extended to 31st October, 2021 for F.Y. 2020-21.
What is the penalty for non-compliance of audit requirements under Income Tax Act
Section 271B of the Income Tax Act prescribes a penalty for non-furnishing of audit report which is lower of ½% of gross receipt or Rs. 1,50,000. Suppose, your gross receipts are Rs. 28 Lakhs. In this case, penalty can be imposed lower of ½% of Rs. 28 Lakhs or Rs. 1,50,000 i.e. Rs. 14,000.
What is presumptive tax scheme for professionals u/s 44ADA
- Presumptive taxation scheme for professionals has been introduced by Finance Act, 2016 for resident individuals and HUF. This scheme is available for those medical practitioners whose gross receipts are not more than Rs. 50 Lakhs. The medical practitioners with gross receipts more than Rs. 50 Lakhs cannot avail presumptive tax scheme.
- If you avail presumptive tax scheme, you can assume your total income from profession as 50% or more of gross receipts.
- If you claim profits lower than 50% of gross receipts and total income is more than Rs. 2.50 Lakhs, in such a situation you will have to maintain books of accounts and get them audited as discussed above.
The medical practitioners have to make decision to opt for presumptive taxation scheme u/s 44ADA on year-to-year basis.
Conclusion:
There are lot of compliances for which medical practitioners need to spare some time out of their busy schedule. In addition to above compliances, they further need to comply with other income tax requirements such as “Advance Tax Payment” on quarterly basis (yearly basis where presumptive scheme opted). So, it is advisable to medical fraternity to get expert advisory and consultancy from qualified professionals so that their tax compliances could be made timely.
For any query or assistance, you may Whatsapp or call on: 09660930417
Disclaimer: The information given in this article is only for education and knowledge purposes and should not be construed as a legal opinion of the author. Readers are requested to seek advice of professional before applying the facts of the above article. Taxwink is not in anyway liable for loss or damage caused to any person on reliance of this article.



